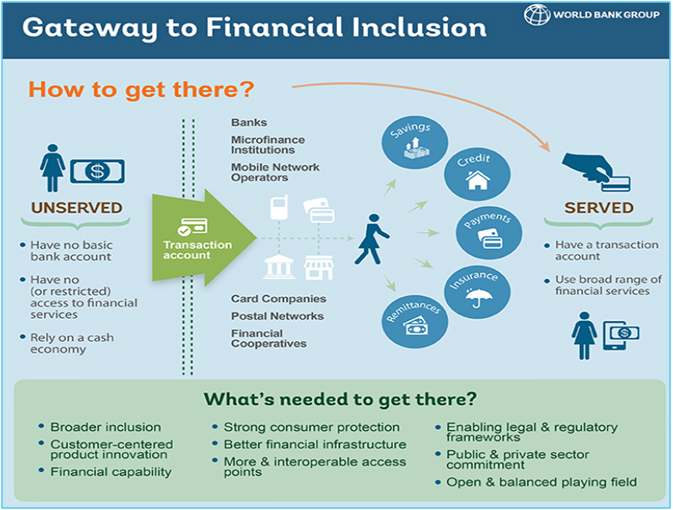
Financial inclusion stands for delivery of banking /financial services to vast section of low income groups (called disadvantaged persons), at an affordable cost. Its objective is to bring the low income group people into banking system, make them bankable customers and develop the banking business. Financial inclusion can be expanded through voluntary effort of banking system and also through the state driven intervention. Financial inclusion is considered to be one of the main objectives of many developing nations since last decade. Financial inclusion is the thrust area of the government and the regulator not only in our country but across the world.
According to the definition by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), financial education is the process by which financial consumers, investors improve their understanding of financial products, concepts and risks, and through information , instruction and /or objective advice, develop the skills and confidence to become more aware of financial risks and opportunities , to make informed choices, to know where to go for help, and to take other effective actions to improve their financial well being.”
Financial literacy means creating awareness among the people about various banking/financial products and services that they have operating knowledge related to each of the products and services and are able to understand risks and rewards to make informed choices. The awareness created through financial literacy enables them to take independent / informed decisions on which products and services to choose from various alternatives available. This will ensure consumer protection which is one of the pillars for financial stability. It is regarded as an important requirement for functioning effectively in the modern society. Raising financial literacy supports financial inclusion and enhances the well being of the community. In India, the need for financial literacy is even greater considering the low level of literacy and huge population which still remains out of the formal financial set up mainly in rural areas.
Financial literacy leads to accelerating the pace of financial inclusion. Understanding the basics of managing money is important for the well being of the people and empowering them financially. The quality and integrity of financial market is improved through financial education. It inculculates saving habit and enable the people to live a better life. Individuals learn planning their expenses against income.Many people live and enjoy their present and do not care for the future. Financial literacy enables people to plan for the present as well as future. A portion of the population in every country is caught in a severe debt trap. A borrower having financial education is unlikely to raise debt which he can’t service.
Many surveys conducted worldwide, point out at the lack of financial literacy in various countries alike all over the world. In the present scenario financial literacy assumes great importance as the financial markets have become more complex. It becomes very difficult to take informed and rational decisions. Financial literacy is therefore very important for promoting financial inclusion and financial stability in the economy. Financial literacy is required in the developed as well as developing countries alike.
Financial literacy plays a vital role in the efficient allocation of household savings and the ability of individuals to meet their financial goals.Reserve Bank of India treats financial inclusion and financial literacy as twin pillars. Financial literacy acts from demand from demand side and it makes people aware of what they should demand. Financial inclusion acts from supply side providing the financial market what is demanded by people. We can say that raising financial literacy enhances social inclusion as well as well being of the people.
The problem we have today in emerging markets / growth markets is that formal financial services are unavailable to consumers. That’s the problem because the low income consumers generally do not know how to manage their cash flows, they don’t have saving accounts. They are not having access to loans, means of transmitting money from one place to another.Today there are more than 2 billion unbanked adults globally who do not have access to banking services.A big part of the world still cut off from banking services.
There is a massive income gap between income of developed and growing countries. The gap is almost five times. Investment in infrastructure that supportsfinancial services in the developing market is lagging.In United States for every one hundred thousand people there are about 200 ATMs. In Canada there are 230 ATMs per lakh population. On the other hand in Barbadoswe have 30 ATMs for every lakh of people. In Trinidad it is 32 ATMs per lakh of population where as it is 29 in case of Jamaica.As compared with the number of ATMs per population there is a high percentage of people with mobile phones. Overhaul of financial services is very much necessary, a complete digital overhaul. Going digital cuts the cost of financial services dramaticallyfractional. Financial inclusion is synonymous with business inclusion.
Recently we have seen huge increase in the use of mobile money. M-pesa is one of the world’s most successful mobile payment systems. More than fifty percent of the transactions done in Kenya is digital. It is the main mobile money system that exists in Kenya. Now around 12 million people use m-pesa to move the money around which is aprrox half the adult population in the country. The usage of cash has declined considerably. Kenya has seen 80 % GDP growth during the last 5 years.
The need of the hour is enabling grass roots, bottom up, inclusive financial services development in growing economies.“Digital banking will bring basic financial services and security to millions in the next 15 years. It will help transform their lives and give the poor more control over their assets .”- Bill Gates, Co Chair of the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. One of the four key areas on which the Gates Foundation is going to focus on is the issue of financial inclusion.
In India a new type of Bank, the Payment Bank was launched in 2015. Payment Bank is a new model of Banks conceptualized by Reserve Bank of India. These Banks can accept a restricted deposit which is currently limited to Rs.100000/- per customer and may be increased further. Loans and credit cards cannot be issued by these banks. Both current and savings accounts can be opened by these Banks. Payment Banks can provide services such as ATM cards, debit cards, net banking, mobile banking etc. India’s first payment Bank has been set up by Bharti Airtel.
For equitable and sustainable development various initiatives in various initiatives in financial sector were taken by the Government and the RBI over the years for increasing banking outreach and ensuring greater financial inclusion. Banks have been advised to leverage the benefits of low cost technology solutions and appoint business correspondents. These agents of the Bank as business correspondents provide doorstep banking in remote areas. Business correspondent channel, as a model of achieving the financial inclusion targets have increased over the past years as the biggest outsourced activity and its importance is growing continuously. The services provided through this are enrolling customer to open account and services such as saving, credit, remittance, insurance, social security, pensions etc. Credit is the most important and vital aspect of financial inclusion.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) was launched for financial inclusion under the National Mission was launched in Indian on 28th August, 2014. PMJDY has also led to the effective implementation of the three social security schemes a) Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY),b) Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) &c) Atal Pension Yojana (APY). The JAM (Jan Dhan- Aadhaar- Mobile)trinity which was proposed in the Economic Survey of 2014-15 is a wonderful initiative to promote financial inclusion in India. JAM trinity is a government of India initiative forlinking Jan Dhan accounts, mobile numbers and Aadhaar cards of Indian to plug the leakages of government subsidies. As per the Department of financial services, Ministry of Finance, 38.89Crores beneficiaries banked so far. Public Sector Banks have contributed to 29.35 Crores beneficiaries, Regional Rural Banks to about 6.29 Crores beneficiaries and Private Banks to approximately 1.25 Crores beneficiaries.Around 1.26 lakh Bank Mitras are delivering branchless banking services in sub service areas in the country.
One of the greatest developments that has taken place in India is that Indian government created IMPS (Immediate Payment Service). IMPS is an instant payment inter-bank electronic funds transfer system through mobile phones. Unlike NEFT &RTGS, the service is available 24/7 throughout the year including bank holidays. RBI is allowing Non- Banking Financial Companies to open White level ATMs. RBI has made a regulation for new branches that 25 percent of new branches are to be in unbanked rural canters.
In the current scenario, financial inclusion has become business imperative and the future lies in leveraging technology based products that are interoperable, having partnership with multiple stakeholders in the eco system, targeting low income, small and micro segments. Partnerships with the stakeholders in the ecosystem of financial inclusion like telecoms, insurance companies, micro finance institutions and consumer goods companies etc would enable the bank to provide end to end solutions, variable products for creating more social impact, economic growth which in turn increases profitability of the financial inclusion initiatives.
BCG estimates that a 1% increase in financial inclusion increased real GDP per capita growth by 3.6%. This multiplier effect looks amazing. Financial education has the potential to become one of the most robust force multipliers that can propel the next growth revolution in the country. As Pranab Mukherjee, said “financial inclusion is a key determinant of sustainable and inclusive growth, which in turn is essential for building an equitable society.
For achieving the objective of universal financial inclusion the delivery model needs to be devised carefully by leveraging technology so as to move from a cost-centric model to a revenue generation model. The services are being delivered through a combination of brick and mortar branch network and network of banking correspondents. Banks or financial institutions alone cannot implement financial literacy. Stake holders for financial literacy consists of: (a) Central government, (b) State governments, (c) Regulators including RBI, SEBI etc., (d) Financial institutions, (e) Educational institutions, (f) NGOs and other social /voluntary organizations . All the stake holders have to play their role and work in coordination to achieve financial literacy.
National Strategy for Financial Education (NSFE): Financial Stability Development Council (FSDC) is a statutory body for ensuring financial stability and financial development in India. This Council is headed by Finance Minister of India. Under FSDC, there is a sub-committee which looks into the financial literacy in India. Taking into consideration the large population of the country and the need for inclusive growth , a focused strategy was conceived by the Government of India, for spreading financial literacy which could also ensure financial stability. This paved the way for adopting a strategy for Financial Education as a project in order to spread financial literacy among people for developing a vibrant and stable financial system in the country. Some of the objectives of the NSFE are:- a) Financial inclusion, financial education and inclusive growth, b) knowledge and skill development, c) freedom from exploitation, d) avoidance of over indebtedness, e) promoting entrepreneurship, f) positive spill-over effects, g) deeper participation in financial markets.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as a regulator has taken various initiatives for improving the financial literacy and commercial banks have supported these initiatives .Financial inclusion and education are two important elements in the Reserve Bank of India’s developmental role. RBI has created volume of literature towards this and uploaded in its website for banks and other stakeholders to download and use. This initiative aims to create awareness about financial products and services, good financial practices, going on digital and consumer protection. Apart from it financial literacy week is held by RBI every year to promote awareness on key topics every year. RBI has also developed tailor made financial literacy content for five target group viz. farmers, school children, small entrepreneurs, self help groups and senior citizens. Various audio visuals have also been designed on topics related to financial literacy for the benefit of the people.
A model scheme of establishing“Financial Literacy and Credit Counseling Centre” was formulated by RBI. Establishment and functioning of the FLCC needs financial support from the sponsoring Banks. The broad objective of the FLCC is to provide free financial literacy /education and credit counseling. FLCC also educates the people in rural and urban areas with regard to various financial products and services available from the formal financial sector. It makes people aware about the advantages of being connected with the formal financial sector. They also formulate the debt restructuring plan for borrowers in distress. FLCC works for promotion of literacy, awareness of the banking services, financial planning and amelioration of debt – related distress of an individual. The government has also set up Financial Literacy Centers (FLCs) and the Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETI) to promote financial literacy in the country.
Comics are provided by RBI on their site which can be downloaded in various languages including Hindi & English. There are videos/films and other materials for financial literacy programmes available on RBI website. Financial literacy material is included in School curriculum to create awareness among school children from the beginning. RBI young scholars award has been constituted to create interest in school students. RBI also conducts exhibitions for promoting financial literacy.
The time has come to realize that the collective efforts of all the stakeholders in the financial sector to provide financial education to the people will go a long way in reducing the NPA and improvement in quality of their assets.It will also ensure stability over a long period of time. Still a lot needs to be done to establish professional Financial Planning standards so that the people can make responsible use of money and credit and make informed financial decisions that affect their family and future.
References:
1 https://www.rbi.org.in
- https://www.oecd.org
- Dr. D. Subbarao. Ex Governor RBI Speech at the RBI- OECD workshop
- https://www.thehindubusinessline.com
- https://www.asianage.com
- https://www.centerforfinancialinclusion.org
- http://www.doglobalgood.org
- https://www.worldbank.org
- i) The article has neither been published elsewhere nor has it been submitted to any other publication, and that I have not reproduced material from any published source except as permitted by the Copyright Act.
.ii) I undertake to indemnify the Bank against any action for any violation of Copyright Act resulting from publication of this article.
iii) Opinions expressed in the article are my own and not of the Bank.
Navin Kumar Singh
Manager (Faculty)
SBILD Bhavnagar,
Vallabhi, Plot No. 2293,
Hill Drive,
Bhavnagar, Gujarat- 364002.
Contact No: 7600057026
PF No. : 3549925.